Initial Price Setting in Retail: How to Kick-Start New Entries
Learn the essential principles of sustainable introductory pricing and find out how it works in practice

Challenge
The wrong introductory price means a failure to bring the expected profits, undermined customer loyalty and brand perception, as well as disbalance in category sales.
The most common factors undermining a retailer’s ability to set the optimal initial price include:
- Misleading reference prices
- Decisions based on gut feeling
- Lack of relevant historical data
- Misperception of consumer behavior

Solution
The right price for a new product is essential for the health of an entire product lifecycle
The right way to price new entries
Sustainable way to set an optimal initial price is based on two factors:
- accurate evidence-based consumer decision tree
- accurate selection of the most similar products sold in the past
The best way to select and analyze similar product sales is to use AI algorithms comparing all products’ credentials (including images, descriptions, etc.) using computer vision, tabular data, and natural language processing.
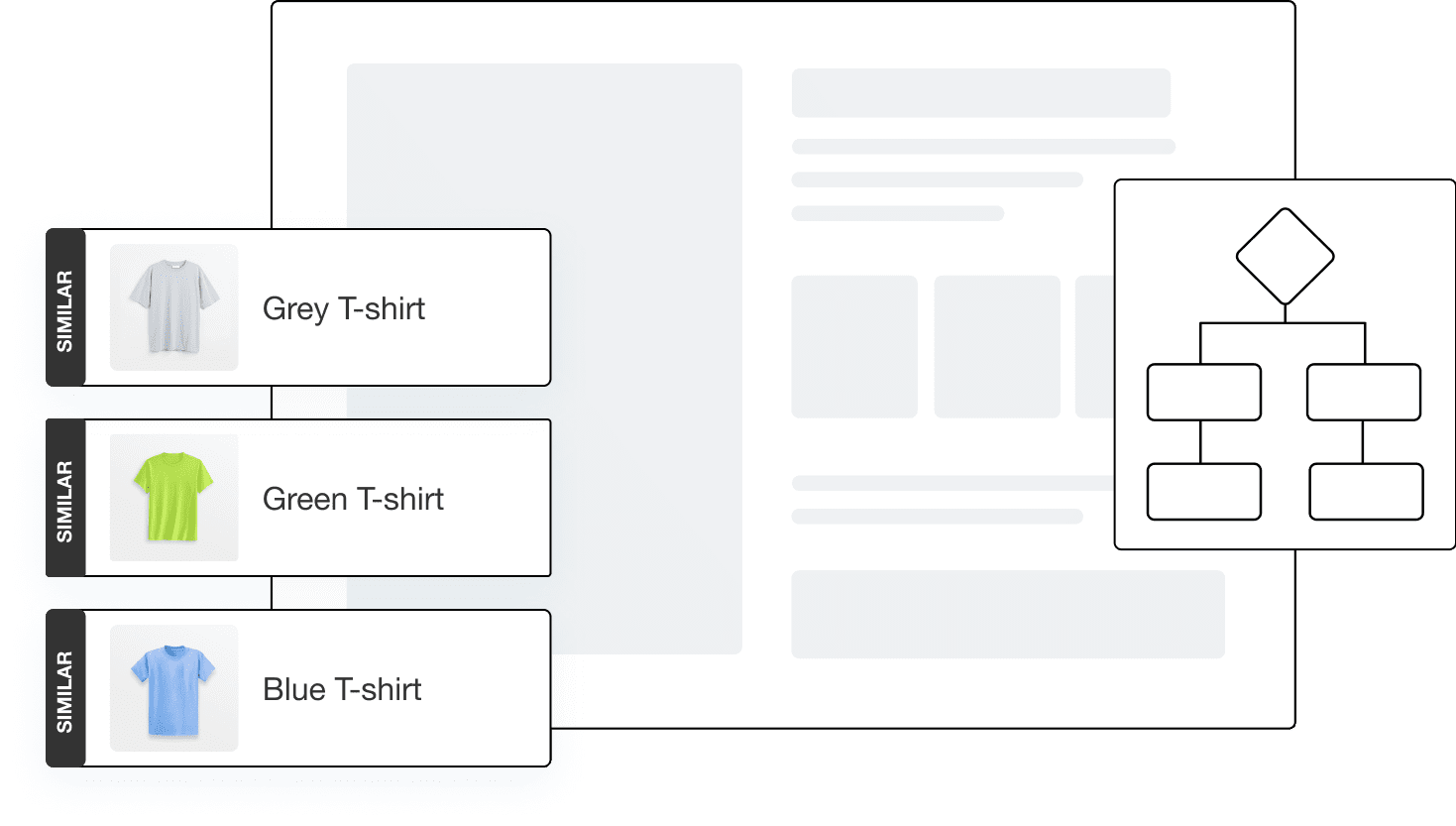
Process data with advanced technology
Once the most similar products are identified, the algorithm correlates a new product with the similar ones. Based on historical sales data, the engine finds the most relevant benchmarks, compares prices, turnover, and elasticity of similar SKU to recommend the initial price for a new entry.
As the algorithm works only with the most similar, yet not identical products, the recommendations cannot be 100% accurate. That’s why identifying accurate shopper decision trees is needed beforehand.
Rely on shopper decision trees
Shopper decision trees help to reveal the shopper path in a category, the way consideration sets are shaped, and importance of prices in the decision-making process.
This, in turn, reveals the boundaries of price tiers for a new product. Direct communication with shoppers via polls and questionnaires is the most reliable way to build an accurate shopperdecision tree.